Subnetting¶
IP subnetting made easy by George Ou has a good overview, here is a summary.
The IP address is a 32 bit number which provides 0 to 4,294,967,295 unique addresses on a network. This is chopped up into 4 8-bit octets separated by a period.
0.0.0.0 to 0.0.0.255 is one octet which provide 256 addresses.
Subnetwork¶
Chopping a large network up into smaller pieces is subnetworking.
- beginning is always even, network id
- ending is always odd, broadcast id
- you can not use the network or broadcast id address, since they have special meaning
- 0.0.0.0/8 (0.0.0.0 to 0.255.255.255) not used
- 127.0.0.0/8 (127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255) used for loop back addresses
- Number of hosts: 2^bits - 2 where bits is the number of bits for the subnet and the -2 accounts for both the network and broadcast id’s
You need to chop along clean binary division as shown below:
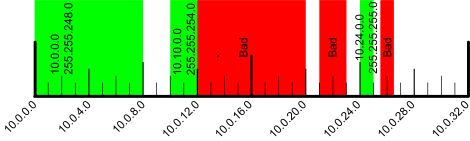
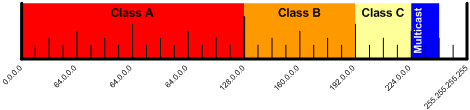
Network Classes¶
| Class | IP Range | Subnet Bits | Mask Bits | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 | 24 | 8 | the first half of the address space |
| B | 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255 | 16 | 16 | half the remaining address space |
| C | 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 | 8 | 24 | half the remaining address space |
| D | 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 | undefined | undefined | half the remaining address space for multicast |
| E | 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255 | undefined | undefined | everything remaining |
Private Subnetworks¶
| Class | Subnet Bits | Mask Bits | IP | IP Range | Number of Hosts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 24 | 8 | 10.0.0.0/8 | 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 | 16,777,216 |
| B | 20 | 12 | 172.16.0.0/12 | 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 | 1,048,576 |
| C | 16 | 16 | 192.168.0.0/16 | 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 | 65,536 |
| C | 16 | 16 | 169.254.0.0/16 | 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255 | 65,536 |
The 169.254.0.0 addresses are only used when DHCP server is not available.
Address Bits¶
- 8 bits = 256 addresses (254 hosts, minus the network and broadcast id’s)
- 9 bits = 512 addresses
- 10 bits = 1024 addresses
- 11 bits = 2048 addresses
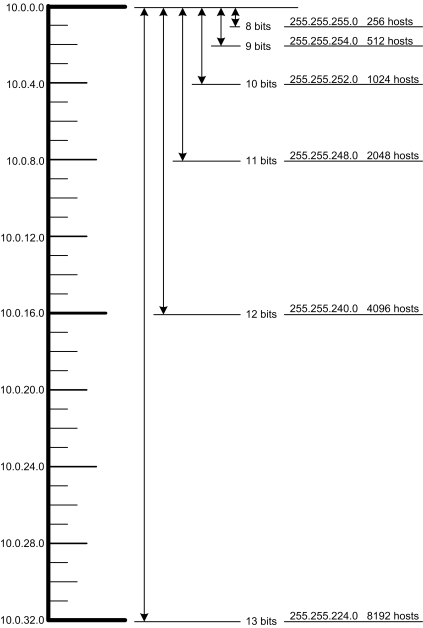
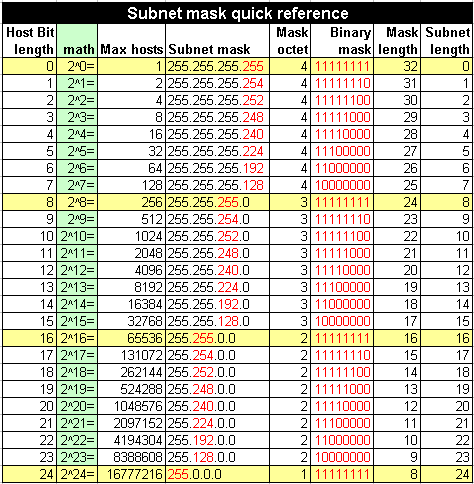
Masks¶
Typical home networks use 192.168.0.0/16 where the 16 indicates a 16-bit mask giving addresses from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255. Since a complete mask is 32-bits and each octet is 8-bits each, 16-bits uses the bottom 2 octets or 192.168.x.x. An 8-bit mask would use the lower 3 octets or 192.x.x.x. A 24-bit mask would only use the bottom octet of the address range, or 192.168.1.x.
- 8-bit mask: 255.0.0.0
- 16-bit mask: 255.255.0.0
- 24-bit mask: 255.255.255.0
Calculator¶
IP address calculator Another one
192.168.0.1/16:
Address: 192.168.0.1 11000000.10101000 .00000000.00000001
Netmask: 255.255.0.0 = 16 11111111.11111111 .00000000.00000000
Wildcard: 0.0.255.255 00000000.00000000 .11111111.11111111
=>
Network: 192.168.0.0/16 11000000.10101000 .00000000.00000000 (Class C)
Broadcast: 192.168.255.255 11000000.10101000 .11111111.11111111
HostMin: 192.168.0.1 11000000.10101000 .00000000.00000001
HostMax: 192.168.255.254 11000000.10101000 .11111111.11111110
Hosts/Net: 65534 (Private Internet)
192.168.1.1/24:
Address: 192.168.1.1 11000000.10101000.00000001 .00000001
Netmask: 255.255.255.0 = 24 11111111.11111111.11111111 .00000000
Wildcard: 0.0.0.255 00000000.00000000.00000000 .11111111
=>
Network: 192.168.1.0/24 11000000.10101000.00000001 .00000000 (Class C)
Broadcast: 192.168.1.255 11000000.10101000.00000001 .11111111
HostMin: 192.168.1.1 11000000.10101000.00000001 .00000001
HostMax: 192.168.1.254 11000000.10101000.00000001 .11111110
Hosts/Net: 254 (Private Internet)